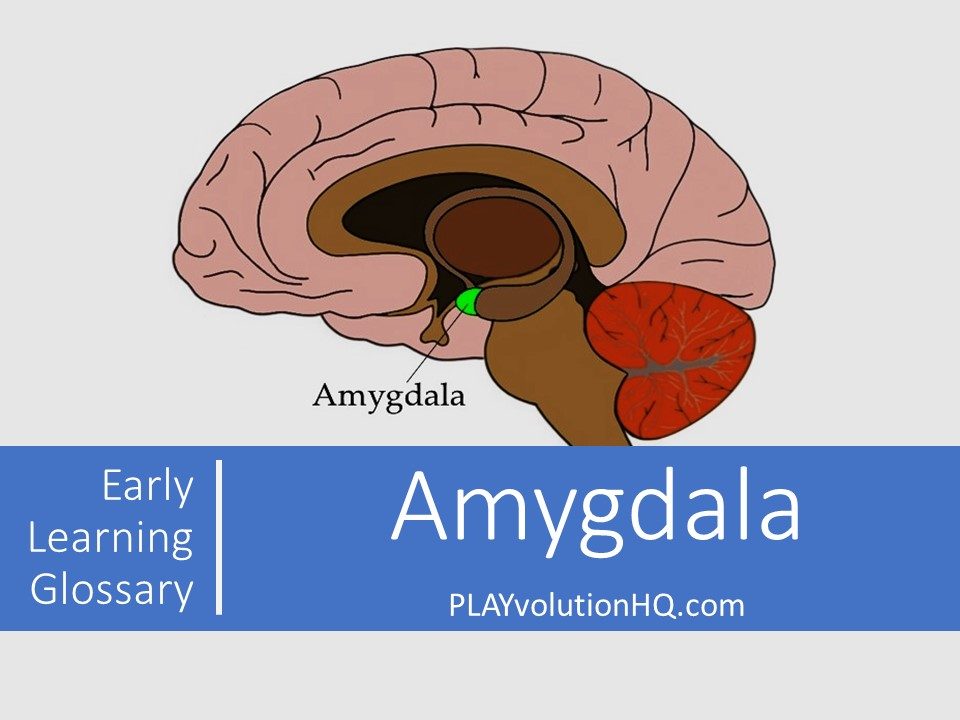
What Is The Amygdala?
The amygdala, a small, almond-shaped cluster of neurons nestled within the brain’s limbic system, serves as a critical hub for emotional processing. Highly responsive to sensory input, it excels at detecting potential threats—a sudden noise, a dark silhouette, or a subtle social cue—triggering the body’s fight-or-flight response through its connections to the hypothalamus and brainstem. As “The Brain Made Simple” aptly notes, “When you think of the amygdala, you should think of one word: fear,” highlighting its starring role in our instinctual reactions to danger. Yet its influence reaches far beyond fear alone.
The amygdala shapes how we experience and respond to a wide range of emotions, from anger and anxiety to pleasure. It plays a key role in emotional memory by enhancing the hippocampus’s ability to store vivid, emotionally charged experiences—like a close call or a heartfelt celebration. It also helps us interpret emotional signals, such as the fear in a friend’s expression, and influences our immediate reactions to the world around us. Far from a one-note fear detector, the amygdala is a cornerstone of emotional learning and reactivity, finely tuning our survival instincts and enriching our human experience.
Videos
Here are three videos that offer more details about the amygdala:
Contribute content to Playvolution HQ
Brought to you by Explorations Early Learning
Thoughts On This Entry?
I’d love to hear your thoughts on improving this entry and suggestions for additional glossary additions in the comments below. You can also contact me with comments or concerns.
Browse Trainings
Post Author
Jeff Johnson is an early learning trainer, podcaster, and author who founded Explorations Early Learning, Playvolution HQ, and Play Haven.


Leave a Reply